
Solar Power Model
What is Solar power System
Solar energy uses the sun’s light and heat to generate renewable or ‘green’ power. The most common form of solar energy is harnessed by solar panels, or photovoltaic cells.
In photovoltaic power stations, they’re arranged almost edge-to-edge to capture sunlight in large fields. You’ll also see them on top of houses and other buildings at times, as well. The cells are created from semiconductor materials. When the sun’s rays hit the cells, it loosens electrons from their atoms. This allows the electrons to flow through the cell and generate electricity.

Types of Solar Power Systems
There are 3 Types of Residential & Commercial Solar Power Systems
On-Grid Solar System

Description:
- The most common type of residential solar system.
- Connected to the public electricity grid.
- Does not include battery storage.
How It Works:
- Solar panels generate electricity during the day.
- Excess electricity is sent to the grid (net metering).
- Homeowners draw electricity from the grid when solar power is insufficient (e.g., at night).
Benefits:
- Lower upfront cost since there’s no need for battery storage.
- Potential to earn credits for excess energy produced (depending on local net metering policies).
- Simple and reliable system.
Off-Grid Solar System
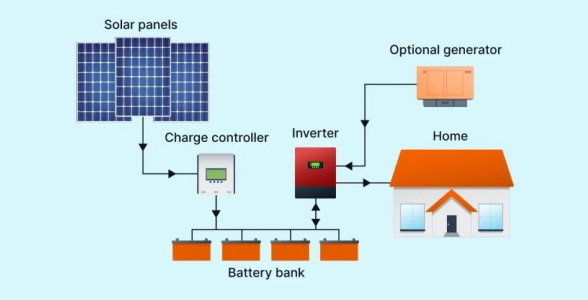
Description:
- Completely independent of the public electricity grid.
- Includes battery storage to store excess power for use when solar production is low.
How It Works:
- Solar panels generate electricity.
- Excess electricity is stored in batteries.
- Batteries provide power when solar panels are not producing (e.g., at night or during cloudy days).
Benefits:
- Complete energy independence.
- No electricity bills.
- Power supply during grid outages.
Hybrid Solar System
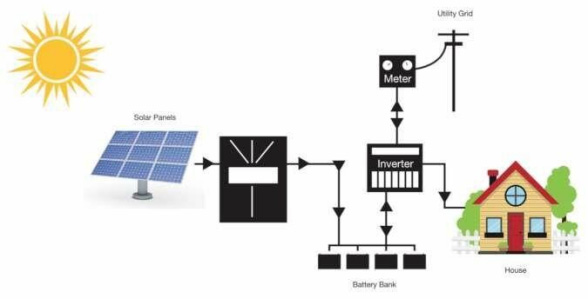
Description:
- Combines grid-tied and off-grid features.
- Connected to the grid but also includes battery storage.
How It Works:
- Solar panels generate electricity.
- Excess electricity charges the batteries and can be sent to the grid.
- Batteries provide backup power during grid outages or at night.
Benefits:
- Flexibility and reliability with both grid and battery backup.
- Reduced electricity bills and potential earnings from net metering.
- Power supply during grid outages.
